Vitargo Sports Drink is the Best choice to Rehydrate, Refuel, Recover
1 February, 2024
Blog
The Forgotten Fuel Source Needed To Boost Performance & Recovery
By: Bernie Wooster

When you’re trying to push in training and it feels like your muscles are tapped out, or you’re slowing down and can’t push into high gear with your endurance…
Maybe your muscles are sore for days on end after a training hard and you feel drained and under recovered going into the next hard training session…
It usually comes down to one important nutritional piece of the puzzle you’re missing the mark on.
Unfortunately, due to bad information aimed at the sedentary general population many athletes avoid this fuel source without understanding the massive benefits it has for them.
As a result their performance and recovery takes a nosedive.
There’s also a ton of benefits from a health and wellbeing perspective when people consume enough of this macronutrient.
This fuel macronutrient has the following general health benefits:
- Improved energy production in the body
- Boosts cognitive function
- Better digestion
- Improved mood
- Helps with falling and staying asleep
- Healthier immune system
Of course the forgotten fuel source we’re talking about is…
Carbohydrates.
Why Is Under-Eating Carbs A Problem For Athletes?

Carbs are the fastest acting fuel for high intensity training whether it’s in the weight room, pool, on the mats or out for longer runs or bike rides.
When you exercise your body uses glycogen – a form of carbohydrate stored in the muscles and liver as the main source of fuel for high intensity training.
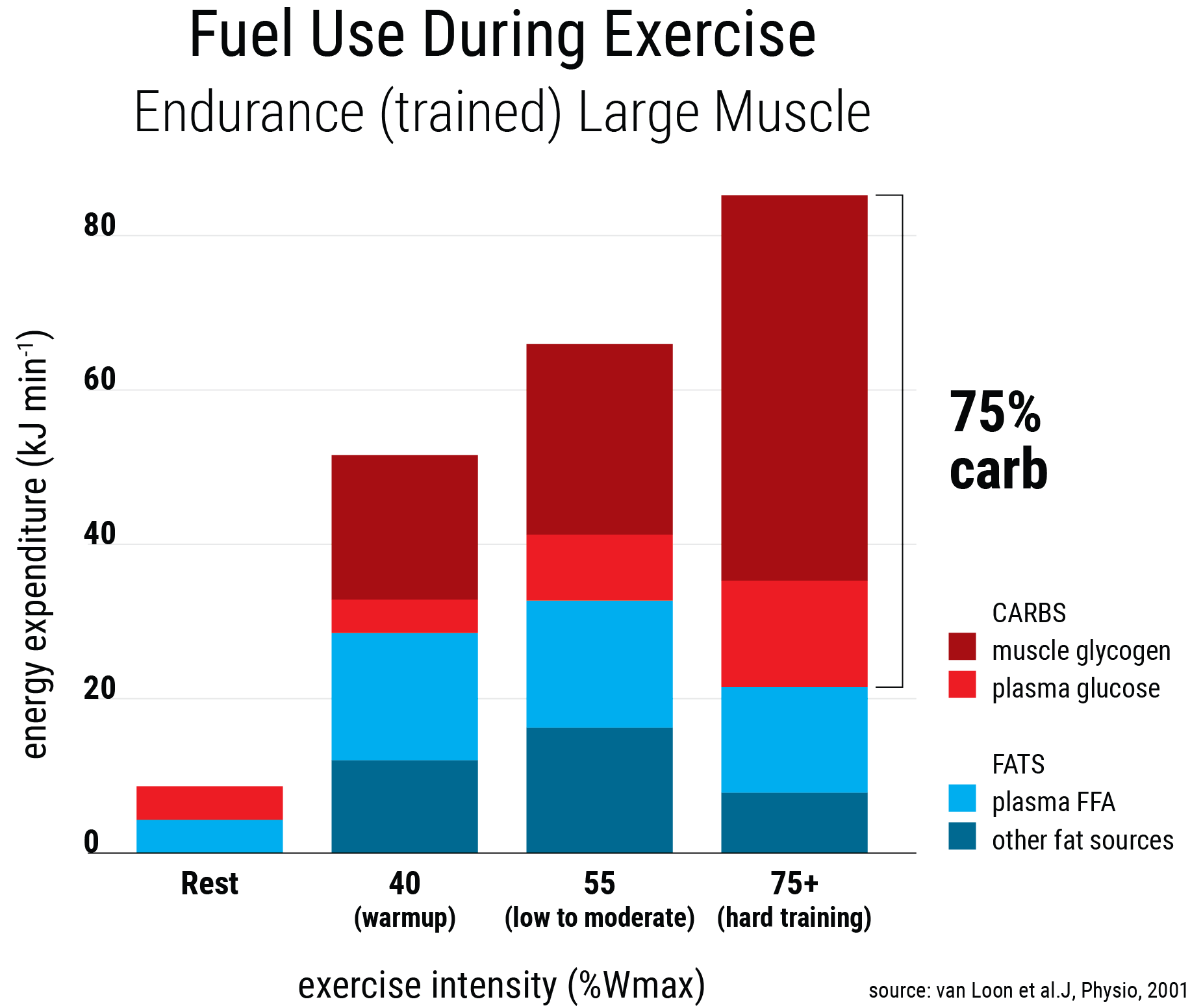
If you don’t consume enough carbohydrates your glycogen stores become depleted leaving your muscles without fuel.
This leads to fatigue, drops in energy and decreased performance.
This can occur during prolonged periods of exercise such as during endurance events or shorter high intensity training sessions like CrossFit, Weightlifting and MMA.
Symptoms of low glycogen from under-eating carbohydrates can include:
Quicker muscle fatigue…
Muscle weakness…
Difficulty concentrating…
Muscle cramps…
Dizziness…
Reduced endurance…
In addition to affecting energy and performance…
Not Consuming Enough Carbohydrates Impacts Muscle Recovery And Repair.

After a hard training session your muscles are damaged and in need of repair, and carbohydrates play a crucial role in this process.
Consuming carbohydrates supports muscle protein synthesis. (the process of rebuilding and repairing muscle tissue)
Carbs help to shuttle the building blocks of protein (amino acids) into the muscles which triggers the process of repairing and rebuilding the muscle.
By under-eating carbohydrates you’re more likely to experience muscle soreness, muscle weakness and a loss of strength in your next session.
Other Problems With Athletes Not Eating Enough Carbs
Aside from feeling weak and fatigued physically many athletes report feeling burned out and having low quality training sessions where the risk of injury increases.
Low carbohydrate intake can affect brain function, and lead to difficulty concentrating and making decisions during demanding training sessions.
Not eating enough carbohydrates before and after a training session can lead to changes in mood, including irritability and feeling anxious.
You’re also more likely to lower immune function making it easier to get sick, and there is an increased risk of muscle loss when not eating enough carbs.
So How Many Carbs Should You Be Eating Each Day?

Using the free calorie and macro calculator linked below is the quickest way for you to get a starting place on how many grams of carbohydrates to be eating.
The macro calculator below will also give you a breakdown of calories, protein and fat if you really want to dial in your nutrition on all home fronts.
The thing to keep in mind is that the numbers from the macro calculator are a starting place, and you’ll need to tweak the plan based on your own needs.
So, now that you know roughly how many grams of carbs to eat, what kinds of foods should you be getting carbs from?
Just like everything in nutrition it really comes down to what works for you because there is no one size fits all in nutrition.
However, below is a list of some common carb sources to consider eating if you know that you need to increase your carb intake.
Quality Sources Of Carbohydrates:
- Whole grains: Whole grains, such as oatmeal, quinoa, and brown rice, are good sources of complex carbohydrates and can provide sustained energy during training.
- Rice: Jasmine or white rice, brown rice, black rice, wild rice, are all great options. People like to argue about brown or white rice being healthier when it’s really a matter of personal preference.
- Starches: Potatoes, sweet potatoes, squash and corn, are good sources of carbohydrates.
- Legumes: Legumes, such as beans and lentils, are good sources of complex carbohydrates. They also contain fiber and some protein as well.
- Fruit: These are good sources of complex carbohydrates, as well as other nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and fiber, that can benefit athletes.
- For athletes who have multiple training sessions or train for longer than 75 minutes: Simpler carbohydrates like honey, rice, pasta, cold or hot cereals and Vitargo can massively help with performance and recovery
Whenever an athlete goes from under-eating carbohydrates to consuming the right amount to meet their demands…
Suddenly athletes feel like they can go the extra reps, rounds and miles while feeling strong and fast.
They feel recovered and refreshed for training sessions so they can increase their work and power output each week.
Athletes can also see changes in their muscle mass and notice that during training they’re able to actually get a pump.
As always at Vitargo we’re here to help and support you however we can so feel free to email us at [email protected]
featured blogs



